India’s Economic Growth: A Shining Exception
The Union Budget 2024-25, presented by Finance Minister Smt. Nirmala Sitharaman, outlines a comprehensive roadmap for India’s economic growth and development. Focusing on employment, agriculture, urban development, energy security, and tax reforms, this budget aims to address the needs of various social segments, including the poor, women, youth, and farmers. With strategic allocations and initiatives, the Union Budget 2024-25 seeks to drive India towards a prosperous and inclusive future.
Despite global economic uncertainties, India’s economic growth continues to be a beacon of hope. Finance Minister Smt Nirmala Sitharaman, presenting the Union Budget 2024-25, highlighted that India’s inflation remains low, stable, and is moving towards the 4% target. Core inflation (excluding food and fuel) stands at 3.1%, with measures in place to ensure adequate market supplies of perishable goods.
Interim Budget Focus: Key Social Segments
The Finance Minister emphasized the interim budget’s focus on four major groups: the poor, women, youth, and farmers. This budget underscores employment, skilling, MSMEs, and the middle class, with a central outlay of ₹2 lakh crore over five years to benefit 4.1 crore youth. This year, ₹1.48 lakh crore has been allocated for education, employment, and skilling.
Budget Priorities: Path to a Developed India
The budget outlines nine priorities to achieve a developed India:
- Productivity and resilience in agriculture
- Employment and skilling
- Inclusive human resource development and social justice
- Manufacturing and services
- Urban development
- Energy security
- Infrastructure
- Innovation, research, and development
- Next-generation reforms
Priority 1: Productivity and Resilience in Agriculture
The government will review the agriculture research setup to enhance productivity. Introducing 109 high-yielding, climate-resilient crop varieties, the initiative aims to support natural farming for 1 crore farmers. Additionally, the budget provides ₹1.52 lakh crore for the agriculture sector.
Priority 2: Employment and Skilling
Three schemes under the Prime Minister’s package will incentivize employment, focusing on first-time employees and supporting employers. The government will also establish working women hostels and creches. A new skilling scheme aims to train 20 lakh youth over five years, with upgraded Industrial Training Institutes and revised skill loan schemes.
Priority 3: Inclusive Human Resource Development and Social Justice
The budget prioritizes economic support for craftsmen, artisans, self-help groups, scheduled castes, tribes, women entrepreneurs, and street vendors. The Purvodaya plan will drive development in eastern India, and the Pradhan Mantri Janjatiya Unnat Gram Abhiyan will improve conditions for tribal communities, with a ₹2.66 lakh crore allocation for rural development.
Priority 4: Manufacturing and Services
Special attention is given to MSMEs and labour-intensive manufacturing. The budget proposes a self-financing guarantee fund, enhanced Mudra loans, and support for food irradiation and safety testing labs. An internship scheme will provide opportunities in top companies for 1 crore youth over five years.
Priority 5: Urban Development
The PM AwasYojana Urban 2.0 will address housing needs for 1 crore urban poor and middle-class families. Water supply, sewage treatment, and solid waste management projects will be promoted in partnership with state governments and multilateral banks.
Priority 6: Energy Security
The PM Surya Ghar Muft Bijli Yojana aims to install rooftop solar plants, providing free electricity to 1 crore households. The scheme has seen over 1.28 crore registrations and 14 lakh applications, with nuclear energy playing a significant role in India’s energy mix.
Priority 7: Infrastructure

The budget allocates ₹11.11 lakh crore for capital expenditure, emphasizing infrastructure development. Phase IV of the Pradhan Mantri Gram SadakYojana will enhance rural connectivity, and financial support for irrigation and flood mitigation projects will be provided.
Priority 8: Innovation, Research & Development
The Anusandhan National Research Fund will support basic research and prototype development. A venture capital fund will expand the space economy, aiming for fivefold growth in the next decade.
Priority 9: Next Generation Reforms
The government will develop an Economic Policy Framework to drive economic development and facilitate employment opportunities. Labour-related reforms will enhance service provision and compliance ease, with a focus on climate finance and simplified foreign investment rules.
Budget Estimates 2024-25
Total receipts (excluding borrowings) are estimated at ₹32.07 lakh crore, with total expenditure at ₹48.21 lakh crore. The fiscal deficit is projected at 4.9% of GDP. The government aims to reduce the deficit below 4.5% next year.
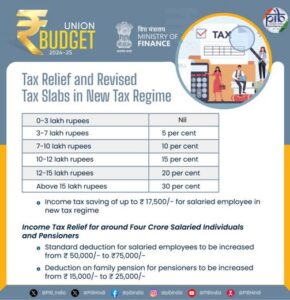
Tax Reforms: Simplification and Relief
The budget proposes a comprehensive review of direct and indirect taxes, GST rationalization, and simplification of the Income Tax Act. Key highlights include increased standard deductions for salaried employees and pensioners, revised income tax slabs, and the abolition of angel tax for investors.
Enhancing Competitiveness and Reducing Litigation
The budget simplifies the tax regime for charities, TDS, and capital gains taxation, aiming to foster competitiveness in various sectors. Custom duties have been revised to support trade and reduce disputes, with specific exemptions and reductions to benefit key industries.
Dispute Resolution
The Vivad se Vishwas Scheme, 2024, will address income tax disputes, with increased monetary limits for filing appeals and streamlined procedures for international taxation and transfer pricing.
India’s Union Budget 2024-25 sets a clear path towards sustained economic growth, social development, and fiscal prudence, promising a brighter future for all citizens.